What if you could design digital experiences while earning $81,000+ annually without stepping into a classroom? The web development field turns this possibility into reality for thousands of Americans. With salaries exceeding the national average by $20,000 and 37% industry growth projected through 2032, this career path combines creativity with financial stability.
Modern businesses need digital solutions more than ever. You’ll master languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create responsive websites and applications. The best part? Many developers work remotely or launch freelance businesses, escaping the traditional 9-to-5 grind.
This guide reveals a step-by-step roadmap for launching your tech career. Discover essential tools, practice through real-world projects, and explore specializations like front-end or full-stack development. We’ll also break down timelines so you know exactly what to expect during your learning journey.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Takeaways
- Web developers earn $81,074 on average in the U.S., with high demand across industries
- Flexible work options include remote positions and freelance opportunities
- Beginner-friendly learning paths require no prior coding experience
- Specialized roles let you focus on design, functionality, or full project management
- Continuous skill development keeps your expertise relevant in evolving tech landscapes
Understanding the Internet and Web Fundamentals
Imagine digital highways connecting billions of devices worldwide – that’s the internet’s core purpose. These interconnected networks let you access information instantly, shop online, or stream videos. Grasping these systems helps you build functional digital products.
What Is the Internet?
The internet is a global network of networks using standardized protocols to exchange data. Servers store website files, while clients (like your phone) request them through browsers. Data travels through cables, satellites, and routers to reach its destination.
How Websites Work
When you type a domain name, DNS converts it to an IP address. Your browser then uses HTTP to fetch files from hosting servers. Three components make this possible:
- Domain system: Translates memorable addresses like “example.com”
- Hosting providers: Store website data on always-accessible servers
- Web browsers: Render HTML/CSS files into visual layouts
This client-server relationship powers every online interaction. Master these concepts, and you’ll troubleshoot issues faster while collaborating with hosting teams or backend experts.
Essential Skills: HTML, CSS & JavaScript
Three core languages form the backbone of modern digital experiences. HTML structures content, CSS styles it, and JavaScript makes it interactive. Mastering these essential skills unlocks your ability to create functional websites from scratch.
HTML & CSS: The Building Blocks of Web Pages
HTML5 provides the skeleton for all web pages, using tags to define headings, paragraphs, and images. Semantic elements like <header> and <article> improve accessibility and SEO. You’ll learn to create clear content hierarchies that work across devices.
CSS3 transforms basic structures into visually appealing layouts. Style properties control colors, fonts, and spacing. Responsive design techniques ensure your creations adapt to mobile screens and desktop monitors alike.
JavaScript: Bringing Interactivity to Life
This versatile programming language turns static pages into dynamic experiences. Handle user clicks, update content without reloading, and create animations. JavaScript works alongside HTML/CSS through the Document Object Model (DOM).
Start with fundamentals like variables and functions. Progress to event handling and API integrations. Practical projects help cement these concepts through real-world applications.
| Language | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| HTML | Structure | Semantic tags, content organization |
| CSS | Presentation | Flexbox, grid layouts, media queries |
| JavaScript | Functionality | DOM manipulation, event listeners |
Focus on writing clean code from day one. Proper indentation and comments make your work easier to maintain. These foundational skills prepare you for frameworks like React or Angular later in your journey.
Front-end vs. Back-end Development Overview
Digital products thrive when creative design meets robust functionality. This dynamic partnership defines modern web development, where specialists focus on either user-facing elements or behind-the-scenes systems.
Key Differences Explained
Front-end developers craft what users see and touch. They transform design mockups into interactive user interfaces using:
- HTML/CSS for structure and styling
- JavaScript frameworks like React
- Cross-browser compatibility testing
Back-end developers build the invisible machinery powering web applications. Their work includes:
- Database architecture and security
- Server-side scripting with Python or Node.js
- API creation for data exchange
Full-stack developers bridge both worlds, managing entire projects from user experience to server deployment. While specializing has advantages, understanding both disciplines improves teamwork and troubleshooting.
Front-end teams focus on performance metrics like load times, while back-end specialists optimize query speeds. Tools differ too:
| Front-End | Back-End |
|---|---|
| CSS preprocessors | Database systems |
| Browser DevTools | Cloud platforms |
| UI libraries | Authentication services |
Collaboration happens through shared APIs and version control systems. Whether you prefer visual design or logical problem-solving, both paths offer rewarding careers in tech.
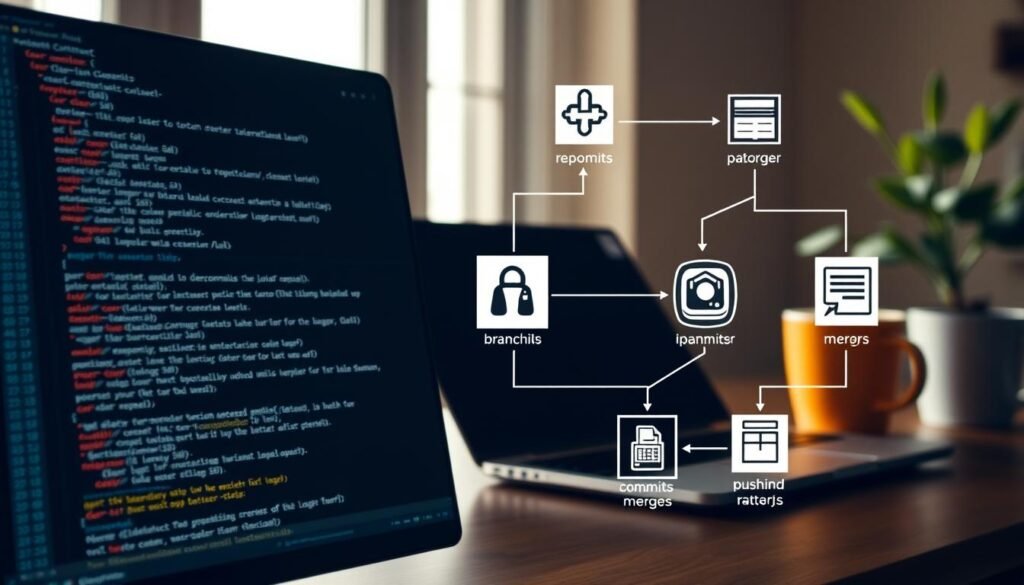
Learning Version Control with Git
Code becomes art when you can reshape it without fear. Git empowers this creative freedom through version control, letting you experiment while safeguarding your work. Over 86% of tech teams rely on this system to manage collaborative projects and track every modification.
Start with core commands that document your progress. git add stages files, while git commit captures snapshots of your code. These actions build a detailed history, showing how your project evolves over time.
Branching strategies prevent chaos in team environments. Create separate branches for new features or bug fixes. This keeps the main codebase stable while you test changes. Merge completed work back into the primary branch using pull requests.
| Command | Purpose | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| git clone | Copy repositories | Start working on existing projects |
| git branch | Manage code variants | Develop features without conflicts |
| git push | Share updates | Sync work with remote teams |
Conflicts happen when multiple developers edit the same file. Git highlights discrepancies, letting you choose which changes to keep. Platforms like GitHub simplify this process with visual merge tools.
Master these tools early to avoid costly mistakes. Roll back errors with git revert or explore past versions using git checkout. Clear commit messages like “Fix header responsiveness” make your history understandable.
Practice collaborative workflows through open-source contributions or team projects. Version control isn’t just about safety—it’s the foundation of professional software creation.
Building Your Programming Foundations
Mastering code requires understanding universal concepts that work across all languages. JavaScript dominates with 75% of developers using it, while SQL handles 47% of database tasks. These tools share core principles that shape digital solutions.
Choosing the Right Programming Language
Prioritize languages matching your goals. JavaScript rules interactive websites. Python excels in data analysis. Java powers enterprise apps. SQL manages information storage. Start with one language before expanding.
All programming relies on four building blocks:
- Variables storing data
- Functions executing tasks
- Conditional statements making decisions
- Loops repeating actions
Understanding Object-Oriented Concepts
Objects group related data and actions. A shopping cart class might track items and calculate totals. Key principles include:
- Encapsulation hiding complex details
- Inheritance reusing existing code
- Polymorphism adapting functions
These concepts help manage large projects. You’ll write cleaner code that teams can maintain. Practice with real scenarios like user authentication systems.
Build logic skills through algorithm challenges. Many developers use platforms like LeetCode to sharpen problem-solving techniques. Strong foundations let you adapt as languages evolve.
How to Start Web Development
Ever wondered what separates successful coders from perpetual learners? Action. Begin with fundamentals like HTML/CSS, then layer JavaScript for interactivity. Coding bootcamps accelerate this process, with 80% of U.S. companies hiring their graduates according to Indeed research.
- Master core languages through interactive tutorials
- Build portfolio projects demonstrating real-world solutions
- Contribute to open-source repositories on GitHub
- Network with tech communities for feedback
- Prepare for technical interviews
Daily 90-minute study sessions prove more effective than weekend marathons. Track progress using tools like Trello:
| Week | Focus Area | Milestone |
|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | HTML/CSS | Responsive landing page |
| 5-8 | JavaScript | Interactive calculator |
| 9-12 | Frameworks | Full-stack prototype |
Choose resources matching your learning style. Structured courses suit methodical thinkers, while project-based platforms help hands-on learners. One developer reported, “Building actual apps taught me more than six months of video tutorials.”
Expect roadblocks – they’re part of the journey. When errors overwhelm, break problems into smaller chunks. Celebrate each working feature, not just completed projects. This mindset shift transforms frustration into measurable growth.
Choosing Frameworks and Tools for Development
Frameworks act as digital blueprints for modern applications, offering pre-built solutions for common challenges. These tools reduce repetitive coding while enforcing industry best practices. You’ll discover how structured environments accelerate development across both interface design and server logic.
Front-end Frameworks: React, Angular, Vue
Modern user interfaces demand efficient component management. React’s virtual DOM optimizes rendering speed, while Angular provides full MVC architecture. Vue strikes a balance with gentle learning curves and flexible integration.
| Framework | Language | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| React | JavaScript | Component reusability |
| Angular | TypeScript | Enterprise-scale apps |
| Vue | JavaScript | Progressive adoption |
Component-based architecture lets you reuse UI elements like navigation bars. One developer noted, “React’s ecosystem shaves weeks off complex projects through shared libraries.”
Back-end Tools: Django, Node.js, Laravel
Server-side tools handle data security and business logic. Django’s “batteries included” approach delivers rapid Python solutions. Node.js excels in real-time applications, while Laravel simplifies PHP workflows.
| Tool | Language | Specialization |
|---|---|---|
| Django | Python | ORM & admin panels |
| Express | JavaScript | API development |
| Laravel | PHP | Elegant syntax |
Consider team expertise and project lifespan when choosing frameworks. Established options offer better long-term support and documentation. Always verify core concepts before relying on abstraction layers.
Optimizing Web Pages for User Experience and Design
Your website’s success hinges on more than just functional code. Over half of global visitors access web pages through mobile devices, demanding flawless adaptability. Master fluid grids and media queries to ensure content reshapes perfectly across smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
User experience principles transform static layouts into intuitive journeys. Prioritize clear navigation menus and readable typography. Test button placements and form fields through prototype tools. Users abandon sites that load slowly or confuse them – optimize both speed and clarity.
Accessibility remains non-negotiable in modern design. Implement ARIA labels for screen readers and ensure color contrast meets WCAG standards. These practices expand your audience while meeting legal requirements. Remember: great design serves everyone equally.
Heatmap analytics reveal how visitors interact with your pages. Use this data to position key elements where eyes naturally linger. Pair these insights with A/B testing to refine layouts continuously. Every pixel should guide users toward their goals effortlessly.
Balancing aesthetics with functionality creates websites people love. Your technical skills now carry creative responsibility – shape digital spaces that feel both useful and delightful. This fusion separates forgettable pages from memorable experiences.